Ivan Čuk
Editorial
Salma Khalfallah, Bessem Mkaouer, Samiha Amara, Hamdi Habacha, Nizar Souissi
EFFECT OF DIFFERING EXERCISE INTENSITIES ON THE RESPONSE TIME OF GYMNASTS AND NON-GYMNASTS IN 3D CUBE MENTAL ROTATION TASK
Laura de Oliveira, Vítor Ricci Costa, Kizzy Fernandes Antualpa, Myrian Nunomura
BODY AND PERFORMANCE IN RHYTHMIC GYMNASTICS: SCIENCE OR BELIEF?
Johanna Weber
ARE THERE CONNECTIONS BETWEEN THE BODY FAT PERCENTAGE, COMPETITIVE RESULTS AND MOTIVATION IN WHEEL GYMNASTS?
Pauline Iglesias Vargas, Fabiana Della Giustina dos Reis, Neiva Leite, André Mendes Capraro
THE SPORTING TRAJECTORY OF ELITE ATHLETES IN ARTISTIC GYMNASTICS: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Elizabeth Allen, Alex Fenton, Keith Parry
COMPUTERISED GYMNASTICS JUDGING SCORING SYSTEM IMPLEMENTATION – AN EXPLORATION OF STAKEHOLDERS’ PERCEPTIONS
Mateja Videmšek, Tjaša Logaj, Gregor Starc, Vedrana Sember, Damir Karpljuk, Ana Šuštaršič
ENERGY EXPENDITURE IN PRESCHOOL CHILDREN DEPENDING ON VARIOUS TEACHING METHODS WHEN PRACTICING THE ABC GYMNASTICS PROGRAMME
Natalia Yu. Tarabrina
PAIRED-CONNECTED DEVELOPMENT OF MOTOR QUALITIES IN AESTHETIC GYMNASTICS
George C. Dallas, Costas Dallas, Μaria Maridaki
THE EFFECT OF 10-WEEK ISOKINETIC TRAINING ON MUSCLE STRENGTH AND GYMNASTIC PERFORMANCE IN PREADOLESCENT FEMALE GYMNAST
Urška Čeklić and Nejc Šarabon
STRENGTH AND JUMPING ASYMMETRIES IN GYMNAST AND THEIR NON-GYMNAST PEERS
Johanna Weber
THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE PERCENTAGE OF BODY FAT AND JUDGING IN GERMAN WHEEL GYMNASTICS
Anton Gajdoš, Michal Bábela
SHORT HISTORICAL NOTES XXII
Ivan Čuk
Editorial
Dear friends,
All gymnastic disciplines were excellent at this year’s Summer Olympic Games. Great achievements of our athletes in artistic gymnastics, rhythmic gymnastic and trampolining! From my subjective point of view, Nikita Nagorny made a huge step forward to further our sport. It took all this time since OG 1988 in Seoul, when Valery Ljukin from the former Soviet Union performed a triple salto backward tucked, to see Nikita Nagorny perform a triple salto backward piked at a major competition. It will take some more time before followers start performing the triple backward piked. However, our science supports and facilitates improvements in apparatus, the development of better methods of strength training, psychological readiness, and so on, and all this leads to further developments in our sport.
Having the Olympic Games and the World Championships within three months of the same year created many challenges for everyone involved in competitive gymnastics. On one hand, there is gymnasts’ tiredness, on another, new faces bring in new energy.
There are new challenges for researchers too. In the middle of October, Flavio Bessi organised International Freiburg Gymnastics Congress online. You can find it at https://www.sport.uni-freiburg.de/en/events/international-gymnastics-congress.
Contributing authors in this issue are from Tunisia, Oman, Brazil, Germany, United Kingdom, Slovenia, Russia and Greece. Again, many different aspects of gymnastics are presented.
Anton Gajdoš and Michal Babela drafted the 22nd short historical note introducing Samulel Piasecky from Slovakia.
Sadly, we lost a gymnastic friend. Aljoša Demjanov who competed for Russia and Croatia passed away last summer. R.I.P., Aljoša.
Just to remind you, if you cite the journal, its abbreviation in the Web of Knowledge is SCI GYMN J.
I wish you enjoyable reading and many new ideas for research projects and articles.
Salma Khalfallah, Bessem Mkaouer, Samiha Amara, Hamdi Habacha, Nizar Souissi
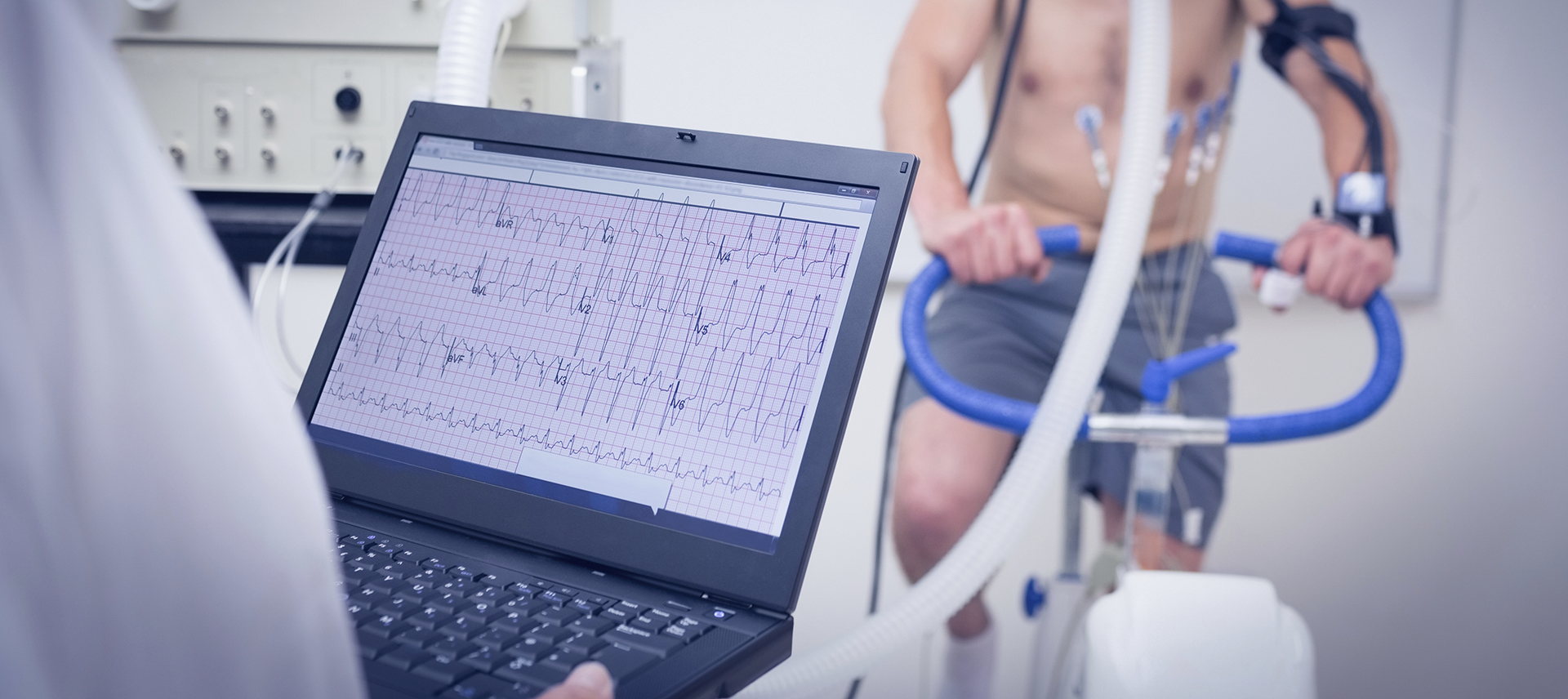
EFFECT OF DIFFERING EXERCISE INTENSITIES ON THE RESPONSE TIME OF GYMNASTS AND NON-GYMNASTS IN 3D CUBE MENTAL ROTATION TASK
The purpose of the present study was to examine the effect of different levels of exercise intensity on mental rotation performance in gymnasts vs. non-gymnasts'. Forty-one participants (18 females; mean age 20.94±0.89 years, height 1.65±0.03 m, body mass 58.94±5.67 kg, and 23 males; mean age 21.26±0.99 years, height 1.70±0.05 m, body mass 66.87±4.52 kg) divided into two groups (i.e., gymnasts and non-gymnast) voluntarily took part in the present study. The two groups performed a 3D cube mental rotation task at rest, and then performed the same task preceded by short bouts of intense exercise at 60%, 80%, 100% and 120% of their maximum aerobic speed (MAS). The analyses of response times showed that gymnasts performed the mental rotation task faster following bouts of intense exercise than in rest condition, especially in 60% and 80% of MAS, whereas non-gymnasts increased their response times after moderate exercises (i.e., 60 et 80 % of MAS) and stabilized their performance (i.e., equally at the rest) after intense exercises. This finding highlights the specific physical expertise as a variable that can affect the influence of exercise on cognitive processing.
Keys words: mental rotation, cognitive processing, exercise intensity, gymnastics expertise.
Laura de Oliveira, Vítor Ricci Costa, Kizzy Fernandes Antualpa, Myrian Nunomura
BODY AND PERFORMANCE IN RHYTHMIC GYMNASTICS: SCIENCE OR BELIEF?
This study aims to identify whether competitive rhythmic gymnasts feel body dissatisfaction and, if so, to analyze the factors related to its development and the implications for the gymnasts’ health. We interviewed 28 female gymnasts, aged between 13 and 16 years, from three teams in one Brazilian state. Based on the thematic analysis, we present the following themes: “Body, Performance, and Misconceptions in Rhytmic Gymnastics (RG)” and “Body weight in RG: Belief vs. Science.” Gymnasts’ dissatisfaction with their bodies appears to be influenced by their coaches, judges, and other athletes, who reinforce the existence of an established “ideal” body type in this sport. The athletes seem to believe that this body ideal would help them in the movements execution in the judges’ evaluation, and would, therefore, influence competitive performance. Their coaches used body mass measured on a set of scales as a reference for controlling and guiding weight loss. To lose weight at all costs, the gymnasts mentioned that they took laxatives and adhered to self-imposed calorie restriction. Excessive pressure to lose weight and obtain results could lead to or maintain body dissatisfaction and damage gymnasts’ health. Thus, coaches must be careful when associating weight loss with better performance; they need to consider the individuality of gymnasts and should not generalize them. Moreover, professional monitoring should be adopted, as well as the use of reliable and justified body evaluation methods. Preventive measures and coach education should also be implemented, and official agencies should regulate and punish any excessive and abusive practices.
Keywords: young athletes, rhythmic gymnastics, body dissatisfaction.
Johanna Weber
ARE THERE CONNECTIONS BETWEEN THE BODY FAT PERCENTAGE, COMPETITIVE RESULTS AND MOTIVATION IN WHEEL GYMNASTS?
Motivation is a performance-limiting factor in sports. Thus, the relevance of motivation for performance in wheel gymnastics must be clarified. 203 German gymnasts were studied. Motivational differences were found between different disciplines and performance levels. Differences between performance levels were also present in groups grouped by discipline. Additionally, a connection was found between hope for success and body fat percentage as well as motivational factors and deductions to difficulty score. Several motivational aspects correlated with age. There were significant correlations between motivational factors and age at different performance levels. Results suggest that motivation might be relevant for the development of talent in wheel gymnastics
Keys words: wheel gymnastics, body fat percentage, judges, competitive results, motivation.
Pauline Iglesias Vargas, Fabiana Della Giustina dos Reis, Neiva Leite, André Mendes Capraro
THE SPORTING TRAJECTORY OF ELITE ATHLETES IN ARTISTIC GYMNASTICS: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Sporting success may be influenced by several factors, the magnitudes of which are revealed throughout the athletes' training process. This study sought to systematically review research that deals qualitatively with the sporting trajectory of elite athletes in artistic gymnastics (AG). The searches were conducted in the Web of Science and Scopus databases, contemplating studies published before July 2020. Data extraction was organized according to the focus and location of the study (context), participants, and methodology used, whereby we analyzed the variables associated with the athletes' trajectory. We located 318 articles and, after applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 15 original studies were selected for the review. The articles used semi-structured interviews with athletes, former athletes, coaches, referees, and managers. In two studies, the authors used methodological assumptions of oral history: one of them documental analysis, and the other ethnography. The systematic review revealed that parental support is essential for insertion and retention in the sport, both for logistical (financing, transportation, organization of school activities) and emotional reasons. Financial support and good training facilities are factors that positively influence success in AG. A healthy relationship between the coach and the athlete is essential, but this relationship is often reported as authoritarian. The post-career phase must be planned and guided so that the transition happens gradually and the athlete is able to seek a new identity.
Keywords: gymnastics, career, athletes, review.
Elizabeth Allen, Alex Fenton, Keith Parry
COMPUTERISED GYMNASTICS JUDGING SCORING SYSTEM IMPLEMENTATION – AN EXPLORATION OF STAKEHOLDERS’ PERCEPTIONS
Gymnastics is one of the original Olympic sports, subjectively judged by humans. Judging errors and bias can occur, resulting in medals being incorrectly awarded. The International Gymnastics Federation (FIG) with Fujitsu are introducing a computerised gymnastics judging support system (CGJSS), a technology aimed to enhance fairness and accuracy but there is very little literature evaluating this technology and perceptions. This project aimed to explore stakeholders’ reactions at this critical time. Therefore, interviews were conducted with coaches, judges, media, former and current international gymnasts. The findings concurred with the literature review of judging problems with the current system, including bias and subjectivity. New findings show, among other things, that gymnasts’ scores can differ depending on which round they compete in. The findings also suggest that the CGJSS would be a great innovation for gymnastics to improve credibility by removing bias and helping to make the sport more objective. However, the majority of the participants believed it could not judge the artistry element of the sport. Close monitoring of the effectiveness of the CGJSS is therefore required to identify enhancement and to ensure the investment produces fairer, more reliable and credible results. Successful implementation of the CGJSS could also allow it to be introduced into other subjectively judged sports.
Keywords: gymnastics, judging, bias, technology, sport.
Mateja Videmšek, Tjaša Logaj, Gregor Starc, Vedrana Sember, Damir Karpljuk, Ana Šuštaršič
ENERGY EXPENDITURE IN PRESCHOOL CHILDREN DEPENDING ON VARIOUS TEACHING METHODS WHEN PRACTICING THE ABC GYMNASTICS PROGRAMME
The aim of the study was to determine whether obstacle course and circuit training are efficient teaching methods as forms of exercise in terms of their intensity, monitored by using energy expenditure measuring devices. The key differences in energy expenditure between the two teaching methods were examined. The BodyMedia SenseWear equipment for measuring energy expenditure was used to acquire data from two practice sessions. A sample of participants included 24 five-year-old children from one kindergarten in Ljubljana, although complete data from both afternoon practice sessions was obtained only from 12 children. The study has shown that obstacle course and circuit training are adequate teaching methods, as moderate to vigorous intensity was achieved with both methods when practicing the ABCs of gymnastics. The average energy expenditure has exceeded 7 MET in the main part of two practice sessions for both obstacle course and circuit training. The results showed no statistically significant differences in energy expenditure between genders or the specific teaching method used.
Keywords: preschool children, ABC gymnastics, energy expenditure, exercise intensity, obstacle course
Natalia Yu. Tarabrina
PAIRED-CONNECTED DEVELOPMENT OF MOTOR QUALITIES IN AESTHETIC GYMNASTICS
Intensification of training and competitive activity in sports creates the need to search and develop new training methods. This study was conducted with the aim to study the influence of the author's methodology of paired-connected development (PCD) of physical qualities on the level of technical readiness and performing skills in aesthetic gymnastics (AG). For 13 girls - gymnasts (12±1.2 years old), training according to the standard method (control group), and 12 gymnasts of the same age and qualifications, using PSD in the training cycle (main group), the level of development of flexibility, strength, speed, coordination, endurance, technical readiness and success of competitive activity was studied. It was shown that the use of PCD improves the flexibility in the hip joints by 4.24% and 2.28% for the right and left legs, respectively, and the flexibility of the spine by 7.04%. Coordination indicators improved by 32.66-41.25%, strength by 10.02%. The increase in speed indicators was 18.71-21.09%, the indicators of special endurance increased by 11.13-25.16%. For balance, the marks increased by 25.75%, for turns by 19.38%, for jumps by 24.58% and for the flexibility movements they increased by 15.47%. The average scores for the technical value of the composition increased from 4.5±0.07 to 5.45±0.06 points (21.1%), and the average indicators of the final competitive scores increased from 14.49±0.04 to 15.73±0.08 (8.56%). As a result of the experiment, the positive influence of the developed PCD methodology on the level of physical and technical readiness of female gymnasts, as well as on the final competitive result, was confirmed.
Keywords: aesthetic gymnastics, coupled method, flexibility, strength, speed, coordination, endurance.
George C. Dallas, Costas Dallas, Μaria Maridaki
THE EFFECT OF 10-WEEK ISOKINETIC TRAINING ON MUSCLE STRENGTH AND GYMNASTIC PERFORMANCE IN PREADOLESCENT FEMALE GYMNAST
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of isokinetic training on muscle strength and gymnastic performance when added to traditional gymnastic training on handspring vault in preadolescent female gymnasts. Twenty female gymnasts with a mean age of 10.50 ± 1.19 years, height 125.50 ± 4.52cm, and body mass 27.30 ± 2.58 kg volunteered to participate in this study. A Cybex II Isokinetic dynamometer was used to measure the peak torque of the knee joint in extension at angular velocities of 60°/sec and 300°/ sec. A Casio EX-F1 (Tokyo, Japan) high speed video camera was placed perpendicular to the optical axis of springboard and vaulting horse. The subjects participated in 10-weeks training for three non-consecutive days per week, 2 hours per day, and separated into two equal groups. The experimental group (EG) followed a specialized training program (technical preparation and muscle strength via Cybex II), whereas the control group (CG) followed the traditional training program (technical preparation and muscle strength). Results showed no significant interaction was found for gymnastic score; however, a significant main effect was found for the time. No significant interaction effect among the three independent variables (group, time, side) was found for the knee extension at 60°/sec. However, the EG had a significantly higher mean values compared to the CG in the post-test. The interaction among the three independent variables with respect to the knee flexion at 300°/sec was not significant. However, the interaction between sides by group was significant. The 10-week isokinetic training added to the traditional training improved the knee strength, which consequently improved aspects of the vault, but did not affect other technical aspects of the handspring performance. Furthermore, results of our study support the claim that optimal performance is the result of a complex interaction of several factors.
Keywords: isokinetic, handspring, vaulting, score, muscular strength, gymnastics.
Urška Čeklić and Nejc Šarabon
STRENGTH AND JUMPING ASYMMETRIES IN GYMNAST AND THEIR NON-GYMNAST PEERS
While many studies investigated inter-limb asymmetries (ILAs) in different athletes, little is known about ILAs in the population of gymnasts. The first aim of our study was to compare differences between gymnasts and their non-gymnast peers in isometric knee maximal and rapid strength parameters (peak torque - PT and rate of torque development - RTD) and countermovement jump (CMJ) parameters (height, maximal force), as well as in ILAs in all outcome measures. The second aim of the study was to assess the relationship between ILA of maximal force and the ILAs of the isometric knee strength parameters. 15 gymnasts (aged 11.19 ± 1.89 years) and 15 non-gymnasts (aged 10.92 ± 1.96 years) performed unilateral isometric maximal voluntary contractions of the knee flexors and extensors on a dynamometer and CMJ on a force plate. ILAs were calculated and compared between groups across all outcome measures. We found that gymnasts reached statistically significant better results than non-gymnasts in most isometric knee strength parameters and CMJ height, but not on RTD of left knee flexion and maximal force in the CMJ. Meanwhile, we did not find significant differences between groups in ILAs. Linear regression showed no correlations between the ILAs measures separately for the groups. Even though we did not find any differences between the groups in the ILAs, we should be aware of it to prevent injury in young girls.
Keywords: isometric knee strength, countermovement jump, artistic gymnastics
Johanna Weber
THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE PERCENTAGE OF BODY FAT AND JUDGING IN GERMAN WHEEL GYMNASTICS
In some sports which focus on aesthetic aspects, such as figure skating, gymnastics and dancing, there is a strong demand for athletes to be and look lean. This demand could lead to pressure on the athletes and cause health problems. It must be clarified whether this is also the case in wheel gymnastics. For this purpose, the percentage of body fat and competitive results of 203 wheel gymnasts (183 female, 20 male, age 21.2 ± 11.9 and 16.8 ± 4.9 respectively; body fat percentage 14.5 ± 3.4 and 8.0 ± 3.7 respectively) were assessed cross-sectionally and tested for correlation between the percentage of body fat and competitive results. Furthermore, their body fat percentage was compared to that of athletes from other aesthetic sports, and it was investigated whether judges might be influenced by percentage of body fat. For this purpose, technical difficulties in training and competition were compared for gymnasts with different percentages of body fat, at the same time taking into account the rating of judges` performance as perceived the gymnasts and their satisfaction with their results. The difference between the technical difficulty during training and competition correlates positively with the body fat percentage (p ≤ .010, r = .268). Gymnasts who are a) not content with judges’ ratings; b) content with their own performance, and c) have a higher percentage of body fat, significantly differed from gymnasts where fewer than three of these parameters were true regarding deductions for technical difficulty (p ≤ .000, η2 = .323).
Keywords: wheel gymnastics, body fat percentage, judges, competitive results.
Anton Gajdoš, Michal Bábela
SHORT HISTORICAL NOTES XXII
































.png)